Search Products
Product Configurators
Language

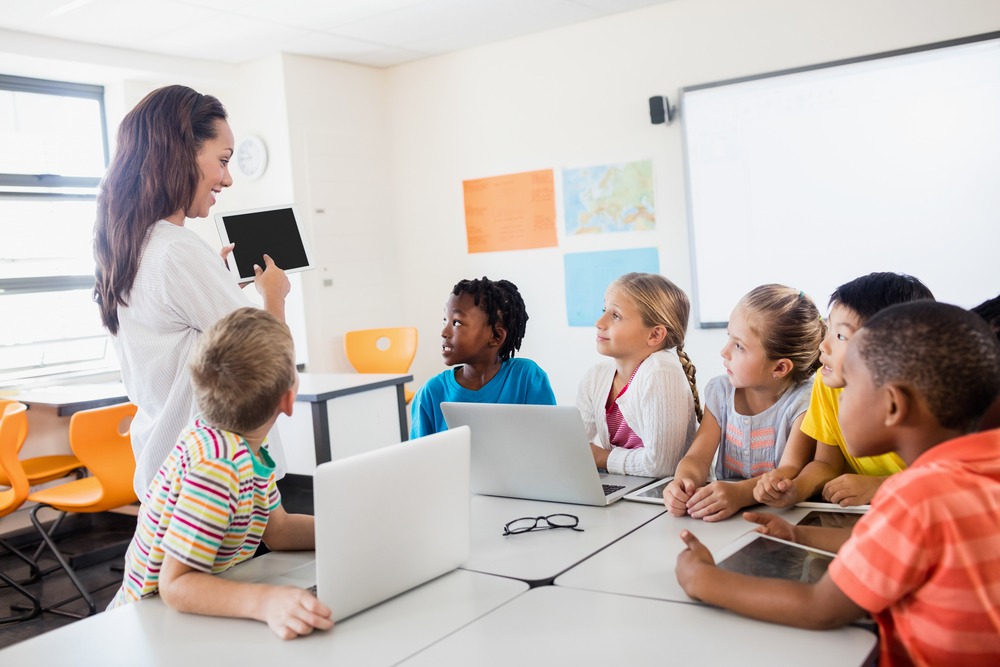
Are you looking for something cheap, durable, and specifically made for the classroom? Well, Chromebooks are all the rage in the classroom right now, and there are multiple good reasons for it too. In this post we will go through all the reasons to consider buying Chromebooks for the classroom, reasons to not consider buying Chromebooks for the classrooms, and other alternatives to consider.
The Good
The first reason to consider Chromebooks for the classroom is its cost. You can get a good Chromebook ranging from $250 to $300. Chromebooks also have an excellent battery life for a day filled with learning.
All Chromebooks come with a special operating system known as Chrome OS. It is a light-weight operating system designed by Google that revolves around the internet. It’s light-weighted nature also helps with increasing the battery life of the device.
Chrome OS comes pre-equipped with all common applications that is required by students. Apps like Google Docs, and Google Slides are used by almost all students to write reports and create presentations.
Students can easily log into Google Classroom to create a collaborative environment with other fellow students and their teachers. There are other apps that are available in the Chromebook that will help students adapt to the modern digital landscape. Typing Club is an app that helps students learn how to type efficiently. “Google for Education” also provides all the necessary apps that allow students to create profiles online and save their work in the cloud. This work can be accessed through any device that is connected to the internet.
Chromebooks are also very easy to use. It relies on the very familiar architecture of the internet and smart phones, which makes it very easy for modern students to pick up.
Chromebooks are equipped for distance learning. This is very important in the current world where remote classes are still held by some schools. Not to mention all the online learning platforms like Coursera, and Udemy which is fully supported by any Chromebook.
When the entire classroom has an internet connected device, you can always play interactive digital games in the classroom. Games in the classroom can make learning fun for children that have attention issues. There are apps like Class Dojo that makes gamifying the learning experience very simple for educators.
Digital resources like Google Arts & Culture are very important resources for introducing virtual field trips in the classroom. Just from their device alone, they can explore art galleries, museums, and more.
An important skill to learn in the modern world is digital notetaking. Chromebooks can be a very easy entry point for students to learn how to take notes. They will learn how to type and listen at the same time. They can also add images, links, and videos to their notes. The notes taken will also be stored online and students will be able to study-up on their notes on any device with an internet connection.
Teaching students how to use a Chromebook effectively will create an army of individuals who will be able to research and learn things on their own. They can be taught the power of the internet where they can research anything and everything that interests them under the sun. Learning to learn will be the most important benefit of introducing Chromebooks in the classroom.
The Bad
The other side of the coin when it comes to Chromebooks is that because they are cheap, a lot of corners are cut by the manufacturers. There are reports by critics that say that Chromebooks are unreliable and tend to malfunction within a couple of years for reasons unrelated to user treatment. Introducing devices that are cheap, and unreliable to millions of students throughout the world might not be the right decision to make when we consider the amount of electronic waste that might be created.
Chromebooks cannot be used in workplaces for the hardcore sciences. To explain the previous statement, we need to understand the workplaces for software engineering, CAD design, artificial intelligence, and research. Professionals of these workplaces will not be able to use Chromebooks for their work even if they want to due to the fact that Chromebooks simply do not support their software applications, or because Chromebooks lack the processing power to handle the amount of compute required.
Introducing students to a stack of software (Chrome OS), that has no application in some important potential workplaces might not be the right decision. This is because they will spend many years getting used to using Chromebooks and their quirks and features but in the end, they will need to learn a completely new operating system and software for their actual work.
The Alternatives
The most obvious alternative to Chromebooks are the cheap Windows laptops. The Windows operating system is the most dominant operating system in the world, so you cannot go wrong in introducing your students to a Windows laptop. If you teach your students video editing, or you utilize games like Minecraft for learning, then using a Windows laptop will be the best choice.
Another alternative is the MacBook line of laptops offered by Apple. Unless your school has a lot of funding, or 100% of your students are rich, you should not push for MacBooks. Although, if you go for MacBooks, it will be the best choice because MacBooks are not only durable, but it can also handle all software and computing tasks thrown at it.
So, What Have We Learned?
Chromebooks are good laptops to consider for students due to their low-cost and versatile nature. You can get all the benefits of an internet connected classroom with a price as low as $250 per student.
On the other hand, Chromebooks are known to be unreliable, and they tend to malfunction within a couple of years. So, it might not be a good idea to consider the hundreds or thousands of Chromebooks that you might have to order for your school.
There are alternatives like Windows laptops, and MacBooks which each have their unique advantages. Windows laptops are good at computing tasks and playing games. MacBooks are perfect for every situation, but they are very expensive.
)
On the 30th of November 2022, a chatbot was released by a company called OpenAI. By January 2023, it became what was then the fastest growing software application by gaining 100 million users. This chatbot caused a hurricane of other competing chatbots that were all trying to do one simple thing, make sense of the world of information found on the internet and every written media on Earth. This chatbot is the Chat Pre-trained Transformer or as it is commonly known, ChatGPT.
In this post, we will go through some of the most imaginative ways in which ChatGPT can be used by teachers and educators alike.
In the Classroom
There are a lot of ways in which you can use ChatGPT in the classroom to enhance the learning experience for students.
You can use ChatGPT to create a teaching assistant for each and every student in the classroom. The teaching assistant could be a sounding board for each student, and it can give constructive criticism when required. ChatGPT can help the students round out their reports or arguments by making sure that their work covers all relevant aspects of the topic. ChatGPT can function as their debate partner, or an interviewer who will test them in different ways.
ChatGPT is especially useful for giving students immediate feedback in terms of their written essays, or their grammar. Students will need to give it very precise prompts by specifying what type of essay they are writing, and what the rubric for the assignment/essay is. When ChatGPT is given specific prompts, it is capable of giving very specific constructive criticism, as well as explain further on the criticism if it is asked to do so.
Since ChatGPT is capable of generating wrong information in some situations, something that is called hallucinations, this is a great time to teach students about critical thinking. They need to be taught that not everything they read from seemingly credible sources are accurate. Students will learn how to cross-check and verify information as well as learn how to do online and offline research.
Another way in which students can use ChatGPT in the classroom is for them to ask it to simplify concepts using pre-existing concepts they understand. For example, “Explain differentiation to me using Lego blocks.” This will help them link different topics, and also have fun while learning.
Outside of the Classroom
ChatGPT especially shines in helping teachers with work not directly related to the classroom.
Teachers can use ChatGPT to make quizzes, and lesson plans. You can get the help of ChatGPT to create fresh quizzes that are not found in textbooks, or to create questions that are culturally relevant. You can always take the generated questions as inspiration and create fresh and better questions from them.
ChatGPT can help you in the classroom by simplifying topics in the classroom. You can always give it a concept and ask it to make it relevant to a specific grade. For example, when you ask it to “explain the theory of electromagnetism to a first grader with just one sentence” it gives the following response, “Electromagnetism is like a magical invisible force that makes magnets stick to some things and helps electricity flow through wires!”
If you are somebody who finds it very difficult to come up with discussion prompts for the classroom, you are in luck because this is where ChatGPT shines. You can always ask it to create good discussion questions for the classroom in any topic necessary, so that your students are always ready to think critically and have a spirited conversation.
ChatGPT also shines at creating handouts, and other materials for the classroom. You can also let ChatGPT generate solved math, or chemistry questions. These questions will most probably not be in the textbooks so it can also be used in tests or exams. The only caveat with generating materials for the classroom using ChatGPT is that you need to cross-check everything personally because language models are prone to hallucinations.
If you do not have the time to write out lengthy e-mails for parents on how their children are performing, they can always jot down quick bullet-points on each child and ask ChatGPT to expand on it. Then the chatbot will create e-mails or short paragraphs on how each child is performing to send to their parent to give it a personal touch. A lot of other written materials can also be written by ChatGPT for your classroom, things like welcome-to-class letters, newsletters, volunteer and donation requests, supply lists, and many more.
ChatGPT can also take in information of each student you have in the class with any relevant data (test scores, participation records, any weaknesses/strengths) and it can give you good recommendations on how to organize certain events. It can help you create groups where everyone has a certain role focusing on their strengths or weaknesses, it can let you know how each student performs in the classroom and what things you need to introduce in the classroom to help them learn better. There are many other ways in which ChatGPT can use the data entered to help you ease your burden. You need to keep in mind that the data entered will go to a centralized server in OpenAI, and you need to understand the relevant laws and regulations for sending your student’s data.
Wrapping It Up
In this post, we looked at ways in which ChatGPT can be used by educators both in and out of the classroom. In the classroom, the chatbot can act as a teaching assistant for each and every student by giving them the attention and care they need when they are learning. ChatGPT can help the students by correcting their essays and improving their grammar.
Outside the classroom, the chatbot can be used to create questions, quizzes, learning materials, lesson plans, letters, e-mails, and much more. Basically, anything that is written down, ChatGPT can help you write. ChatGPT can also help you personalize the classroom by processing some basic data of each and every one of your students and helping you organize groups and create activities for your students focusing on their strengths or weaknesses.

Are you a teacher, or school management who is looking to use technology to improve the quality of education but don’t know where to start? Then you need to read this post where we describe an incredible framework to do just that. The Intel Skills for Innovation (SFI) Framework is a framework that you can use to integrate technology to your programs and plans for cognitive, technical, and socio-economical skill development. You can use this framework for physical, as well as virtual learning environments.
In this post, we will investigate the path to adopt the SFI framework. The steps involve planning, experiencing, training, and deploying.
Planning
The planning stage of the framework involves anticipating the need for change, preparing for the expected changes, responding to sudden disruptions, and adapting to incremental changes on the education system.
Your students will undergo anywhere from 12-14 years of formal school before tertiary education or entering the workforce, hence, it is very important to keep tabs on the various trends on education for the next decade in the least. For this very reason alone, your education institute needs to understand the future of education.
A future-facing educational system needs to have a future-proof vision where it is not only ready for anything that might happen in the future, but actively supporting change in the educational technology space. Everyone involved in running an educational institute will also need to understand potential changes in the future and will also need to understand how to make their institute resilient to all the changes by not fighting it, but by creating a strategy on how to adopt changes as it happens.
Experience
The experience stage of the framework is included in the Intel SFI Starter Pack learning experience. This is the stage where educators experience technology-infused skill-building activities first-hand. All 70 activities used in various curriculum subjects are presented to the educators of that specific subject.
Each activity contains an educator’s guide, a teaching deck, and working files. The educator’s guide has pre-defined learning objectives, lesson overview, activity guide, troubleshooting tips, and assessment and rubrics for the activity. The teaching deck contains an introduction to the topic, hands-on activities, guided learning, discussion topics, and reflection topics. The working files contain worksheets, installation guides, applications, source files/codes, and data sets.
For the educators who are not tech-savvy (not all of us are), there are various beginner guides provided by Intel where there are basic guides on how to use and apply the guides, activities, and technologies with greater confidence.
Training
The training step of the framework is included in the Intel SFI Professional Development. This learning experience empowers educators to assume their role of adapters of technology to mentors of upgraded mindsets. This transition is captured in four steps: adapter, owner, catalyst, and mentor.
The adapter step is for new educators who have not been introduced to technology in the education sector yet. This step helps all educators build a basic fluency in education technology through a mix of face-to-face and online modules.
The owner step transitions the educators from being an active learner to an active leader in the learning experience. This involves making them familiar with remote learning, creating a healthy relationship with the machines who will act as co-educators, engaging with students in the digital age, and strengthening real-world relevance in the classroom.
The catalyst step is the step where the educators are made to imagine new ways in which technology can be used to reimagine learning experiences. They will be taught how to think analytically through data, think critically to make better decisions, and they will be taught how to bridge the gap between creativity and analytical thinking.
The mentor step involves introducing the educators to the upgraded mindsets resulting from the Fourth Industrial Revolution. They will also be taught how to navigate the future of technology that is turbulent at best. This course will explain what it is to have an Agile Mindset, and how it will affect the teaching and learning environment. It will also teach them strategic thinking where the educators will be taught how to think divergently where multiple scenarios can be created through one situation. It will also teach them how to develop plans for each possible future. This step also includes understanding the science behind curiosity, and it will teach educators how to harness the powers of curiosity in their learners to make them into innovators and forward thinkers.
Deploy
The final step of the framework is the deployment step where everything that the educators have learned is deployed in the real-world. Intel has an SFI Learning Platform where educators and administrators can access a rich, interactive social learning environment where they can learn, share, collaborate and connect to a global population of educators.
If there are any problems in the deployment of any of the activities involved in the framework, the good people in the learning platform will always be ready to help you.
Wrapping It All Up
In this post, we discussed a framework on how to introduce technology in the classroom. This framework is called the Intel Skills for Innovation Framework. This framework is divided into four easy steps which are planning, experience, training, and deploying.
Planning involves everything involved with planning the future of your educational institute with a vision that withstands the changing tides of technology.
Experience includes a learning experience where educators are brought into the world of the students and made to experience the new education technology landscape through the eyes of a beginner.
Training includes all the steps involved to create a trained professional who has successfully transitioned from a student into a full-fledged educator of new minds.
Deployment involves bring your new skills into the real world by introducing your students to it. It is the final step and there are tens of thousands of educators around the world who are with you in this step through the SFI Learning Platform.

In the emerging educational landscape, Educational Technology, or EdTech, is playing a crucial role in revolutionizing special needs education. From bridging accessibility gaps to creating individualized learning experiences, EdTech has emerged as the linchpin of inclusive education. It has the potential to transform the learning experience for learners with varying disabilities, making education far more productive and engaging. Here's an in-depth look at how EdTech is reshaping the landscape of special needs education:
1. Individualized Education Programs (IEP):
The 'one-size-fits-all' approach in education is increasingly becoming redundant. EdTech fosters a shift towards more personalized learning experiences, enabling teachers to create individualized education programs (IEPs) that cater to each student's unique challenges and strengths. Disability-specific digital curriculums, adaptive learning software, and customizable lesson plans ensure that learning experiences are tailored to each student's abilities and learning preferences, thereby facilitating a more effective and engaging learning process.
2. Leveraging Assistive Technologies:
Assistive technology has been pivotal in minimizing barriers for students with dyslexia, visual impairments, speech impediments, or hearing loss. Innovative solutions like screen readers, speech-to-text programs, and text-to-speech software imbue a sense of independence in learning for these students. For instance, a student who struggles with handwriting can harness the power of speech-to-text tools to document their thoughts and responses, thereby focusing on the learning process rather than the barriers.
3. Interactive Learning Tools:
Children with special needs can benefit immeasurably from tactile and interactive learning experiences. EdTech provides a treasure trove of such experiences – interactive whiteboards, gamified-learning apps, virtual reality, and tactile touchscreens kindle engagement and make learning a tangible, enjoyable journey. Such tools soften the barriers of learning and make learning experiences not just memorable, but also impactful.
4. AI-Powered Therapy and Counseling:
AI-driven educational platforms have been instrumental in making therapy and counseling services accessible, affordable, and diverse. From speech therapy tools for learners with communication disorders to social story apps for those on the autism spectrum, these technologies transcend mere academic support to provide essential therapeutic interventions.
5. Promoting Social Integration:
EdTech offers a multitude of tools that encourage collaboration and teamwork, fostering vital social skills in students with special needs. Engaging in joint activities in shared digital spaces can play a key role in building their communication skills, making them more confident for social interactions beyond the classroom.
6. Accessibility Tools:
Embedded within mainstream technologies are numerous accessibility tools that offer significant support to learners with disabilities. Keyboard shortcuts for those with motor impairments, voice assistants for visual impairments, and display accommodations like high contrast or large text for low vision are just a few possibilities. These tools enable students to access digital content in an environment tailored to their learning needs.
7. Real-Time Progress Tracking:
By capturing and analyzing data in real-time, EdTech equips teachers and parents with valuable insights into the academic progress of students with special needs. This continuous assessment allows for early identification of potential issues and enables timely intervention and support, resulting in a far more effective learning process.
8. Fostering Parental Involvement:
EdTech platforms uphold the indispensable role of parental involvement through parent-teacher communication tools. They keep parents updated about their child's progress, upcoming classroom activities, and any necessary adjustments. Fostering a coordinated effort between teachers and parents is crucial for a child's educational journey, especially for those with special needs.
While the transformative potential of EdTech in special needs education is impressive, it's crucial that its implementation is done strategically. It is vital to ensure that the chosen technology aligns with each student's specific needs, and educators are well-trained to make the most of it. The classroom infrastructure, too, needs to support the effective use of such technologies.
In conclusion, EdTech, when harnessed effectively, holds the promise of making education more inclusive, accessible, and equitable. With the right tools and strategies, it can catalyse an enriching, personalized, and empowering education for learners with special needs, providing them an invaluable key to unlock their full potential. As educators, parents, and policymakers, it’s our responsibility to optimize the incredible potential of EdTech to redefine the landscape of special needs education for the better.

The digital age has revolutionized the educational panorama with its bountiful advances, and indubitably, social media is one of its most dynamic contributory factors. With ubiquitous platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and YouTube, the world is no longer confined to physical boundaries but is a global village teeming with information and interaction. Through these platforms, learning experiences and knowledge dissemination have been thrust into a new era characterized by collaboration, interaction, and engagement. This, however, brings in a nuanced challenge; integrating social media in the classroom effectively and wisely to primarily focus on education and to create a secure and empowering digital sphere for students.
To give a detailed understanding, let's navigate through the multiple benefits and strategic ways to employ smart usage of social media in the educational domain.
Expounding the Benefits of Social Media in the Classroom:
1. Connectivity and Collaboration: Social media breaks down the walls of the physical classroom, enabling students and educators to interact seamlessly. This offers a landscape conducive to the sharing of information, ideas, and updates. It encourages collaborative projects and group assignment work, utilizing shared digital spaces like Google Drive, aiding in the development of students' communication and teamwork skills.
2. Engagement and Participation: Modern educators can leverage social media tools to enhance student engagement and participation. This can be as simple as setting up a class Facebook group for lively discussions, triggering debates on current affairs on Twitter or sharing didactic resources on YouTube. This adds a new dimension to learning, complementing traditional modes, and making education more interactive and dynamic.
3. Real-World Skill Development: Navigating social media platforms with responsibility instills digital literacy and Internet safety awareness among students. In today's digital world, these skills are imperative, so introducing social media in the classroom serves a double purpose - of combining education with digital readiness, hence preparing a future ready workforce.
4. Parent-Teacher Communication: Platforms such as Facebook or Twitter can serve as meeting junctions for teachers and parents. Prudent use of these platforms allows for timely updates on classroom activities, homework assignments, and general announcements. It takes parent-teacher communication to a new level, ensuring transparency and bridging communication gaps.
Strategizing Smart Usage of Social Media in the Classroom:
Enhancing learning experience with social media comes with a unique set of challenges, hence strategizing its smart usage becomes significant.
1. Set Clear Guidelines: Develop a comprehensive social media policy that specifically outlines acceptable behaviors, content sharing rules, privacy settings, and the consequences of policy violation. Open discussions about this policy can create a safe and respectful online culture.
2. Educational Platforms: Rather than mainstream platforms, opt for the educational versions of popular social media apps that are designed keeping in mind the safety and focus of students. These platforms minimize distractions and regulate content, thus providing a secure and controlled environment.
3. Privacy is Paramount: It's crucial to hold sessions on privacy settings on social media platforms, thus educating students to use them effectively to safeguard their personal information. Respecting the privacy of students is pivotal when teachers share content or updates on these platforms.
4. Monitor Use: It's important for educators to keep a check on students' social media activities to ensure they are adhering to guidelines and using platforms productively. This also serves as a barrier to preempt cyberbullying, creating safe online spaces.
5. Teach Digital Citizenship: Consciously integrate lessons on digital citizenship, teaching students to use social media ethically, responsibly, and with respect for others. By doing so, we not only empower them with knowledge but propel them to become sensible digital natives who adopt a balanced approach to technology.
In conclusion, if employed smartly, social media can metamorphose the complexion of the classroom, elevating learning experiences and helping students to foster better relationships with their material, peers, and instructors. By implementing a thoughtful, discerning strategy, we can harness the abundant potential of social media for the cause of profound and productive education, while simultaneously mitigating potential distractions and risks associated. This pivot to a digitally enhanced pedagogy could be pivotal in molding the future citizens of our digital global village.

As EdTech continues to revolutionize traditional teaching methodologies, e-learning platforms have emerged as pivotal tools in promoting accessible, personalized and engaging learning experiences. However, with a myriad of options flooding the market, it can be daunting to select the right fit. In this post, we'll review and compare some of the top choices to aid your decision-making process.
1. Google Classroom
Google Classroom, part of the Google Workspace for Education, facilitates quick assignment creation, distribution, and grading. The platform is seamlessly integrated with other Google tools like Google Docs and Google Drive.
Advantages: Easy-to-use, versatile, excellent collaboration capabilities, and it's free for schools.
Disadvantages: Lacks a comprehensive built-in student assessment system.
2. Canvas
Canvas is lauded for its open, intuitive design and cloud-based system. It provides features such as content sharing, grading, feedback, and integrates with numerous educational apps.
Advantages: High customization, seamless app integration, and robust community support.
Disadvantages: The learning curve for newcomers, and advanced features can be overwhelming for some users.
3. Moodle
As a free and open-source platform, Moodle provides various tools for collaborative learning. It boasts features like forums, databases, and wikis to create customizable courses.
Advantages: High levels of customizability, extensive plugins, and add-ons, and it's open-source.
Disadvantages: Requires technical expertise for setup and configuration, and the interface isn't very intuitive.
4. Blackboard
Blackboard, one of the pioneers in the e-learning industry, offers interactive learning experiences with features like data reports, grading, and customizable assessments.
Advantages: It's feature-rich, offers various learning modules, and has built-in student assessment capabilities.
Disadvantages: The user interface isn't as friendly as others, and it can be costlier than competitors.
5. Coursera
Coursera partners with top universities and organizations worldwide to offer online courses, professional certifications, and complete degree programs.
Advantages: Accessible high-quality content from renowned institutions, diverse offerings.
Disadvantages: Some courses require a fee, and peer-reviewed assignments depend on the course and students' commitment.
In conclusion, the ideal e-learning platform largely depends on individual or institutional needs. While Google Classroom is great for K-12 and integrates with familiar tools, platforms like Canvas or Blackboard may be more suited for higher education. Moodle's customizability could work perfectly for specific requirements, but Coursera serves those seeking expert-directed instruction. As you review these platforms, remember what's most important is ensuring your chosen platform resonates with your teaching approach and caters to the diverse needs of learners.
In our evolving digital age, technology-driven education, or EdTech, is revolutionizing the traditional landscapes of learning across the globe. From personalized learning tools to massive open online courses (MOOCs), EdTech is unlocking new realms of global accessibility, interactivity, and inclusivity in education. However, with the expanding reliance on this growing field, the significance of potential cybersecurity risks escalates. This dependence underscores the urgency to comprehend the importance of cybersecurity within the realm of EdTech and to be proactive in applying the best practices.
Understanding the Importance of Cybersecurity in EdTech
As reservoirs of extensive and sensitive information, education institutions manifest as attractive potential targets for cyber threats. With the integration of EdTech solutions, cybercriminals seize opportunities to exploit any breaches in security systems. The imperative nature of EdTech platforms' security is crystal clear in our current digital education environment.
The criticality of cybersecurity in EdTech primarily revolves around these key aspects: data privacy, system integrity, and student safety:
1. Data Privacy: Educational institutions manage a trove of sensitive information, encompassing personal details, academic records, and financial data of students, faculty members, and administrative staff. An absolute assurance of data privacy is paramount to the survival, sustainability, and trustworthiness of these institutions. Risks associated with breaches are not only harmful but can also damage the institution's reputation.
2. System Integrity: Cybersecurity breaches pose a tangible risk to the integrity of educational systems. Any disruptions caused by these invasions can lead to losses in valuable resources, time, and ultimately, education quality. A well-secured system, hence, guarantees a consistent and robust operative infrastructure, enabling academic activities to persist without hindrance.
3. Student Safety: The digital well-being of the younger generation is of utmost importance. With more young minds venturing online, exposure to dangerous content or harmful online interactions has become an area of significant concern. A securely designed EdTech ecosystem ensures that students can navigate the digital education space safely and beneficially.
Best Practices for Ensuring Cybersecurity in EdTech
Designing and implementing a secure EdTech environment is not an overnight affair. It necessitates thoughtful planning and astute execution of robust security measures. Below are some key strategies to consider in the goal of steadfast cybersecurity:
1. Regularly Update and Patch Software: Ensuring all software, systems, and applications are regularly updated with the latest patches and security fixes is essential. Cybercriminals capitalize on known but unpatched vulnerabilities to execute unauthorized access.
2. Robust Password Policies: Encouraging faculty, staff, and students to utilize complex and unique passwords changed on a routine basis is a simple yet effective security measure. Incorporating multi-factor authentication (MFA) can provide an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access, even when passwords get compromised.
3. Secure Wi-Fi Networks: Institutional Wi-Fi networks should be well-secured to prevent unauthorized access. Implementation of strong encryption protocols and secure private networks can act as a significant barrier against potential cyber threats.
4. Regular Security Audits: Performing periodic security audits are a proactive step toward identifying and rectifying vulnerabilities in the system. These audits act as early warning systems, enabling the institution to handle any security hazards with immediate effect, ensuring minimal damage.
5. Foster Cybersecurity Awareness: Instituting a comprehensive cybersecurity curriculum and arranging regular training sessions for students, teachers, and non-teaching staff can significantly elevate the overall security environment within the institution. Education and awareness are powerful tools in preventing breaches.
In conclusion, the amalgamation of cybersecurity and EdTech has escalated from being just an option to an indispensable requirement for modern educational institutions. The essence of continual vigilance and responsiveness to potential cyber threats can ensure a robust and secure learning environment. This focus on cybersecurity not only elevates the safety standards but also enhances the overall growth, trust, and reputation of educational institutions in today's diverse and dynamic digital landscape.

In an era ruled by smartphones, the introduction of mobile learning or m-learning in educational technology (EdTech) is revolutionizing learning experiences. Here's how the transition to small screens is shaping the education sector:
1. Ubiquitous Learning:
Learning is no longer constricted to classrooms or desktop computers. With educational apps, e-books, video lectures, and interactive exercises on mobile phones, students can now learn anywhere and at any time, making education truly ubiquitous.
2. Personalization:
Many mobile learning apps offer personalized learning paths based on the learner’s abilities and preferences. Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms analyze a learner's progress and automatically adapt content to suit their pace, understanding, and performance levels.
3. Gamified Learning:
Mobile EdTech has successfully gamified learning. Apps with multiplayer quizzes, puzzles, simulations, and digital rewards have made learning interactive and fun, thereby increasing student enthusiasm and participation.
4. Diverse Learning Materials:
M-learning provides easy access to a wide array of content through podcasts, videos, infographics, and text, all in the palm of your hand. This variety caters to different learning styles and needs, enhancing the overall learning experience.
5. Peer Interaction:
Many mobile learning platforms incorporate social learning features, allowing learners to collaborate, discuss and learn from each other. This peer-to-peer interaction enhances comprehension and establishes a vibrant learning community.
6. Instant Feedback:
Mobile learning apps provide real-time feedback to learners. Whether it's an educational game or a practice quiz, immediate results and feedback techniques help learners understand where they stand and how they can improve.
7. Lifelong Learning:
Mobile learning isn’t just for K-12 or college students. With professional development courses, language learning apps, and hobby-related lessons readily available on smartphones, m-learning supports continuous learning throughout a person’s life.
8. Reduction in Educational Disparity:
The affordability and accessibility of mobile phones can help bridge the digital divide. Virtual classrooms on mobile apps can reach students in remote locations, thus making quality education more accessible and reducing educational disparities.
However, like any other technological revolution, the mobile learning revolution has its own set of challenges. Internet connectivity, digital literacy, and maintaining student focus in a distraction-prone device are some of the hurdles to overcome.
Despite these challenges, with careful planning and effective execution, the mobile learning revolution shows immense promise. It’s clear that smartphones, when used effectively, can become powerful educational tools. As we adapt to this evolving educational landscape, it’s exciting to see how learners use this technology to further their education, skills, and knowledge.

Over the past several years, an emerging digital revolution has completely disrupted and dramatically transformed the educational landscape. This transformation is grounded in a phenomenon often referred to as Educational Technology, or EdTech, which has steadily taken on the mantle of defining the direction of future classrooms. EdTech is no longer an optional extra, but an essential component of modern learning. Its influence radiates across every facet of teaching and learning, from the amplification of the traditional classroom setup to becoming a pivotal platform for distance learning. The diversity and relevance of EdTech are ever-evolving, becoming more critical with each passing day.
So, what does this technological metamorphosis mean for the future of education? Let's delve deeper into the progressively vital component that modern education has come to rely on.
1. Personalized Learning Experiences:
One of EdTech's most exciting offerings is its undeniable potential for personalization in learning. Adaptive learning systems, one of the shining stars of the EdTech repertoire, curate a unique educational experience that is tailored for each student on an individual level. It aligns with their pace, comprehends their context, and responds to their distinct learning style. In a very real sense, such systems create a personal learning pathway for each student.
Not only does this provide a comfortable learning pace for students, but it also empowers instructors with the ability to monitor individual progress. It allows them to pinpoint academic strengths and weaknesses, adjust instructions in real-time, and personalize interventions to maximize student performance.
2. Enhancing Teacher Efficiency:
Importantly, the story of EdTech is not about rendering teachers obsolete but about enhancing their capabilities and augmenting their influential roles within the educational ecosystem. Cutting-edge EdTech tools streamline and automate administrative tasks that can be burdensome and time-consuming. This frees up valuable time for teachers, allowing them to focus on their primary commitment: instructing and mentoring their students.
Furthermore, digital platforms create unlimited access to a treasure trove of educational resources, instructional materials, and reference libraries. These resources are invaluable for lesson planning, curriculum development, and the continuous refinement of teaching methodologies.
3. Collaborative Learning Environments:
EdTech extends its influence beyond individual learning by facilitating seamless collaboration within the learning community. Innovative platforms like Google Classroom enable group projects, digital discussions, peer reviews, and collaborative problem-solving exercises. These activities not only improve academic performance but also aid in fostering vital teamwork skills and enhancing social interaction among students. Breaking down the physical boundaries of classrooms, these platforms orchestrate a vibrant, interactive global learning network, casting a broad, international perspective on student learning experiences.
4. Integration of STEAM Learning:
Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Math (STEAM) education finds a natural ally in EdTech. The integration of interactive activities, immersive online games, virtual labs, and digital art tools make the exploration of complex and abstract STEAM subjects not only manageable but-worth noting-exciting. Coding platforms, for instance, demystify programming concepts, while online simulation tools offer practical experiments beyond the physical constraints of traditional laboratory settings.
5. Lifelong Learning and Continuous Professional Development:
One of the most fundamental truths about education is that it no longer remains confined within the school years. EdTech bolsters the concept of lifelong learning and encourages continuous professional development by offering online courses, certification programs, and opportunities for self-paced learning. This means, for teachers, the opportunity for continuous professional development, upskilling, and staying updated with the latest educational trends and pedagogical techniques is just a few clicks away.
6. Bridging the Accessibility Gap:
EdTech has a profound social dimension to it. It is instrumental in democratizing access to quality education and creating an inclusive learning environment. The advent of assistive technologies has heralded a new era where learning difficulties for students with disabilities are being mitigated. Customized tools and resources aimed at supporting diverse learning needs are making education possible for all, thus bridging the accessibility gap.
7. Data-Driven Education:
The power of data analytics, driven by AI and machine learning, is an integral part of EdTech’s offering. It can sift through vast sets of data related to student performance, unearthing deep insights that can guide evidence-based teaching strategies, curriculum improvements, and policy decisions. These data-driven strategies go a long way in refining the educational process, leading to overall enhancement in educational outcomes and student success.
In conclusion, the transformation brought about by EdTech in modern classrooms signifies the increasingly digital future of education. As we journey deeper into this future, ongoing research, relentless advancements in technology, concerted educator training, and judicious resource allocation will be crucial factors in ensuring a seamless, effective, and inclusive implementation of EdTech.
Regardless of the obstacles and challenges that come our way, one conclusion stands out as an irrefutable truth: EdTech is here to stay, and it will continue to shape and redefine learning experiences in ways that were unimaginable even a few short decades ago. As we move towards an era marked by a fusion of education and technology, we stand on the brink of an education system that can be truly customized, inclusive, and universally accessible.
Generation Z—those born after the mid-to-late 1990s—are digital natives who have grown up in a world of smartphones, social media, and constant connectivity. To engage this dynamic generation, education needs to be as interactive, collaborative, and tech-savvy as they are. Enter game-based learning, a potent aspect of educational technology (EdTech), perfectly suited for engaging Gen Z. Let's explore why.
1. Immersive Experiences:
With game-based learning, education transcends traditional lecture-based instruction. Games can take students on historical adventures, scientific explorations, or mathematical quests, captivating them with immersive experiences, storylines, and challenges.
2. Boosts Engagement:
Games by their nature are engaging, and applying that to education has the same effect. Game-based learning mixes fun with instruction, keeping Gen Z learners invested in their educational journeys, thereby improving their concentration and intrinsic motivation.
3. Enhances Retention:
Game-based learning promotes active participation, pushing students to apply the information they've learned to solve problems or reach in-game goals. This process improves knowledge retention and understanding of complex subjects.
4. Encourages Collaboration:
Multiplayer educational games foster teamwork. Gen Z, known for valuing collaboration and social consciousness, can work together, share strategies, and learn from each other, promoting a healthy, collaborative learning environment.
5. Instant Feedback:
Most educational games provide immediate feedback, making learners understand their mistakes right away and learn from them. This immediate reinforcement is effective in bettering concepts, improving skills, and promoting a growth mindset.
6. Develops Essential Skills:
Aside from subject-specific content, game-based learning also promotes the development of essential 21st-century skills. These include problem-solving, critical thinking, creativity, digital literacy, and adaptability, all within a low-risk environment.
7. Personalized Learning:
Game-based learning naturally offers personalized instruction. A student progresses through the game at their pace, tackling challenges that match their current level, creating a personalized, self-paced learning journey.
8. Promotes Inclusivity:
Game-based learning does not discriminate. Regardless of ability, everyone is on equal footing in a game. This inclusive nature of gaming can help level the playing field in education, aiding in achieving academic equity.
EdTech is revolutionizing the way Gen Z learns, and game-based learning stands at the forefront of this transformation. While this presents manageable challenges like ensuring digital equity and controlling screen time, the benefits are substantial. By integrating gaming elements into education, we can keep Gen Z learners active, engaged, and invested in their learning process while equipping them with the skills they need for the future.

In our present digital era, data has become a fundamental element for smart decision-making and strategic planning across all sectors, including education. As an invaluably effective tool, data analytics in education has the capacity to dissect and analyze complex data sets, revealing significant insights regarding student performance, teaching methods, and curriculum efficiency. This investigation takes a deeper look into the vast and transformative impacts of data analytics upon the world of education.
1. The Advancement of Personalized Learning:
Data analytics has revolutionized the way we approach education by allowing for a highly customized learning experience. By analyzing complex algorithms from data sets, educators can tailor curriculum and learning paths that cater to individual learning capabilities, pace and performance. This breakthrough in adaptive learning provides an effective way to enhance the teaching process and offers students a more rewarding and personally tailored learning experience. Moreover, personalized attention to student needs has the potential to foster greater student engagement, thereby promoting an increased retention of information.
2. Proficient Tracking of Student Progress:
Data analytics sheds light on student progress over fluctuating periods, offering an unparalleled insight into student development. Not only does this help educators pinpoint specific areas where a student may be facing difficulty, but it also illuminates their strengths. Teachers can therefore balance their focus between addressing areas of difficulty and encouraging students to cultivate their areas of strength — forming a well-rounded learning experience that covers all bases.
3. Early Intervention Possibilities:
One of the major advantages of data analytics in education is the ability to formulate accurate and specific analysis of student data. This ability enables educators to identify and provide early interventions to students who may be at risk of falling behind. Whether this indicates a need for additional tutoring, curriculum adaptations, or alterations in the teaching methodology, these early interventions can be invaluable to a student's overall academic achievement.
4. Curriculum Development and Enhancements:
Data analytics is frequently employed by educational institutions during the crucial process of curriculum development. Institutions use this methodology to determine what topics should be included in the curriculum and how these topics should be taught. By assessing the effectiveness of different courses and modules, they can continue to develop a curriculum that balances student needs and prevailing industry trends.
5. Efficient Resource Allocation:
Institutions can also optimize their management and allocation of resources using data analytics. By identifying where existing methods are successful and where further improvements can be made, schools can reallocate their resources - time, finance, or human resources, with increased efficiency.
6. Strategies to Improve Student Retention:
Data analytics enables schools and universities to identify patterns and factors contributing to early student dropouts. Equipped with this understanding, institutions can introduce proactive measures to enhance student retention rates, fostering a positive learning environment.
7. Assessing Teacher Effectiveness:
Data analytics serves a critical role in assessing the effectiveness of educators. By examining student performance data and student feedback, school administrators glean invaluable insights into the efficacy of different teaching methods and aids. These insights allow for targeted professional development and teacher training, ensuring the continual growth of educators.
8. Guiding Policy Making:
On a wider scale, data-driven insights from educational institutions can significantly impact policy-making. Governments and policy makers can use the information to understand major trends, craft strategic education plans, introduce educational reforms, and evaluate the effect of these changes over time.
Notwithstanding its enormous potential, the field of data analytics in the education sector is not without its set of challenges such as safeguarding data privacy, promoting data literacy, and ensuring a reliable technology infrastructure is in place. Addressing these challenges is vital to enable the successful implementation and to maximize the benefits of data analytics in education.
In conclusion, the use of data analytics signals a momentous shift in the way we perceive and navigate the realm of education. It lays the groundwork for a more equitable, tailor-made, and efficient learning system, further reinforcing its indispensability to the future of education. This evolutionary process redefines the education landscape where every student has equal access to quality education that's personalized to their individual learning styles.

Short-form video and social media content is arguably the dominant source of communication for many young people today. With the rise of TikTok, YouTube Shorts, and Instagram reels, students today consume exorbitant amounts of content. A 2022 Pew Research Center survey revealed “Almost half of US teenagers aged 13-17 say they are online ‘almost constantly’”. This raises concerns among educators about media literacy and whether students possess the skills to understand how social media is constructed. Because of this, secondary educators may consider integrating social media content creation as part of student assessment. One tool to help empower student creators is Canva.
Canva is growing in popularity among individuals, teams, and a wide range of industries as a tool for constructing professional communications. The site offers design capabilities so anyone can create products from logos to presentations to social media with ease.
Canva for Education is loaded with resources and tutorials to help teachers and students alike. The site has continually evolved over the past few years to meet the needs of remote teaching and learning. One stellar communications platform that they offer is their talking presentations. The design and template library offers teachers eye-catching aesthetics that are bound to keep students engaged.
Here are some other ideas for what teachers can get out of Canva:
- A platform for creating classroom posters. Choose your side, opt for a template, and create away. Classroom rules, word walls, reminders…the possibilities are endless. The site allows you to download PDF versions to print to your school’s color printer with ease. Save them in classroom management folders and print them fresh the following year!
- Use the platform to design effective parent communication. Templates allow for thoughtfully-designed newsletters that can easily be linked within mass emails to keep families in the loop. Your communications are bound to stand out with Canva’s contemporary aesthetic.
- Consider creating a “class brand”. Because Canva allows you to create communications for so many occasions, using the same fonts, colors, and shapes to develop a cohesive feel. Canva offers lots of options for logos, which could make your email signature dynamic and distinct.
Empowering Students as Media Composers
Aside from the practical (and frankly, fun!) tools Canva offers teachers for a modern classroom, it’s a platform that allows students to build their confidence in designing text and design that can be influential in their world. While there is a time and place to teach and assess a text-only assignment, many would agree that visual communication skills are rising to the top of sought-after abilities. The more practice and experience that students can gain in considering visual composition along with writing effective text, the better they’ll be able to serve future employers across so many fields. In April 2022, NCTE released a position on media education in the ELA classroom, asserting “All learners need to be able to express themselves using writing, speaking, and visual representation using varied modes, genres, and platforms of communication. These competencies are essential to work, life, and citizenship, impacting who has access to conversations, who can speak, and who is heard.”
So, how can teachers offer these opportunities for students?
Well, one of the stand-out creation tools of Canva is their hub from creating social media, posts, reels, and stories. The first step in incorporating social media creation into the classroom is to learn about the genre itself. Start the unit or project by examining various campaigns across different platforms and use the opportunity to broaden students’ vocabulary of media literacy. On their site, Common Sense Education, provides numerous articles and resources to help you launch your discussion.
Here are a list of questions that might help springboard class analysis of social media across platforms:
- What do you notice about the pictures used? What emotions do they convey?
- What motion graphics are used? How do they hold your attention?
- What text did the writer include? What impact do the words have?
- What do you think the content creators want you to feel after viewing this post/reel/story?
- How was the video produced? Does it look like it was made by a professional or by a user? (user-generated content)
- Why do you think this works or does not work as a post/reel/story? Would it have been better suited to be another form? (This could be a fun application exercise; have students transform a short-form video to a still post, or vice versa!)
- Does the design of the media match the brand of the organization? How do you know?
- How does the caption impact the message?
- What, if any, hashtag does the writer use? Is it effective?
- Who do you think is the intended audience of this post/reel/story?
By using these close analysis questions, students will start to see the intention behind the content. This, of course, will inherently build their ability to compose something on their own. Social media analysis could take place over a course of a few days, especially for higher level secondary students who you may want to expose to potential career paths in various fields such as communications, advertising, marketing, and media. Video content creator is a growing, in-demand job, as discussed in this recent Forbes article.
Once students are ready to create content, they can head to Canva and create a free account. If they are creating posts, they choose posts; if you want them to create short-form video, there are a number of different options for templates including Instagram stories and YouTube video. Students can create a project from scratch or choose a template, especially helpful for those just starting out. The “play” button in the top right corner will show students how long their video is according to the motion graphics and video reel that they drag in to include. Students can import original video or choose from high-res, royalty-free stock footage seamlessly embedded from Pixabay into the Canva platform. Once students are done, they can simply download their content to their Google Drive and share with the class with ease.
Give Canva a try to empower students as the next generation of content creators. They’re bound to engage with this easy and fun platform for novice or experienced designers!
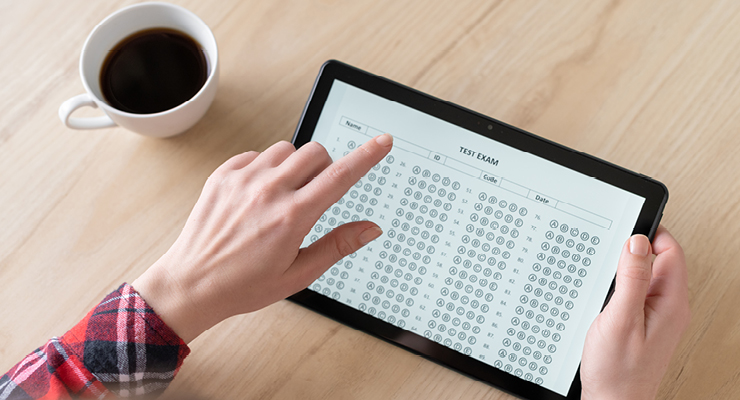

Standardized testing is meant to give an unbiased report of every student’s learning progress which in turn makes the scores comparable. Although currently, standardized tests have become anything but standardized. In this post we will go through reasons why standardized testing has become the bane of students, we will also talk about some alternatives to standardized testing that you as a teacher can apply in the classroom, and finally, we will talk about how technology can help students perform better at standardized testing.
What’s Wrong with the Way We Do Things Currently?
If it isn’t broken, don’t fix it. Many people go with that adage for most things in life but there are many cons when it comes to standardized testing that you really need to pay attention to.
Teachers are meant to teach students and anything straying from the most efficient teaching in the classroom is a step in the wrong direction. When standardized testing is introduced in the classroom, more time is spent preparing the tests rather than preparing for lessons.
When everything a student does hinges on the test results being good, it can cause students to be stressed. This was even more pronounced during the pandemic when there were various sources of stress on the students which then affected their test scores. All these reasons can cause the performance of students to be negatively affected.
How Can Technology Replace Standardized Testing?
Standardized testing is supposed to measure the learning progress of students. If we take the fundamental reason why we need standardized testing (measuring the learning progress of students), we can then use that concept to design the ideal classroom around it.
There are many intelligent adaptive technologies with embedded assessment technologies that provide enough data for the progress that a particular student has made in the classroom. There are technologies like Dreambox that give predictive insight into the performance of a student in standardized testing.
There are various remote learning software that tracks students and their progress. They provide so much data on the performance of students that the students might not need any form of standardized testing to gauge their progress.
Technology to Prepare for Tests
Although technology provides a way to completely do away with standardized tests, it will still take time to get everybody on board. So in this section, we will go through some methods that you as a teacher can help your students perform better in standardized tests.
You can start by familiarizing your students with the type of questions a standardized test contains. Educational technology tools like ClassTime can help you create multiple-choice questions that provide immediate feedback to your students. This will make sure that they will not freeze up during the day of the test.
A theme that almost every standardized test follows is critical thinking. Critical thinking is a very important trait that every person needs to develop and the classroom is the perfect place to start. Critical thinking can be developed through discussions and debates in the classroom. You can divide your students into groups and give a particular topic for them to discuss. Ideally, the students will then debate and discuss in their respective groups about the topic. They can then be tasked to create slides to present their discussions. The way that they evaluate, analyze, and synthesize various ideas in the group will cause them to use the same process in the standardized tests.
One way to improve the understanding of concepts in the classroom is by showing students how what they are currently learning connects to the real world. You can connect history with science, physics with chemistry, and math with computer science. The world is interconnected, and it falls on the lap of the teachers to show the students how all the subjects they learn are connected on a foundational level. Connections help students understand more, which then improves their performance in all standardized tests and exams. 3D printers can be used to teach various physics concepts, computer applications can be used to teach math and computer science. Integrating technology to teach cross-curriculum connections can be as simple as showing them a YouTube video on a specific topic.
You can also use data analytics to tailor your teaching techniques to the requirements of the classroom. Platforms like Classtime lets teachers export excel sheets for individual students. It includes performance metrics for each student that can be tracked throughout the year. If you analyze the data, there will be many gold nuggets of information hidden in the data. You can then check up on individual students and see if they need help in any particular subject, or you can give them additional material to help them perform better. A teacher taking extra time to learn more about their students through data analytics can help the students learn more effectively, which will finally contribute to them performing well in standardized tests.
Conclusion
Standardized tests are a way to measure the progress a student has made in their learning journey in a comparable fashion. Ideally, a standardized test allows students to showcase how much they have learned. In the current times, standardized tests have fallen out of favor for many people in education. The tests have become a be-all and end-all for students, and everything a student has worked towards culminates in a couple of tests. This causes undue pressure and stress for students. There are various educational technologies that can replace standardized tests in the classroom. Technologies like embedded assessment technologies and various remote learning software allow teachers to get a clear outlook on the students in their classroom and their respective progress.
Since standardized tests are here to stay, for the time being, teachers can utilize various educational technologies to help them perform better in the tests. There are various applications online that allow you to mimic the style of standardized tests, like multiple-choice questions. Teachers can also teach critical thinking skills in the classroom by introducing discussions and debates, they can integrate cross-curriculum connections in their lessons to make the lessons more understandable. Finally, a teacher can use learning applications that collect data from the students, which can then be used to analyze the performance of each student.

Classrooms around the country are gravitating towards Book Creator as a tool to give voice, design authority, and ease of sharing to students and educators alike. With over 100 million books created on the platform, it’s clear that Book Creator’s intuitive platform and educator-friendly features provide an asset to K-12 classrooms.
Essentially, Book Creator is a content creation tool specializing in eBooks. Like many design platforms, Book Creator offers a free and paid version, depending on your needs and budget. Teachers can create eBooks for students to access and read during a lesson, or students can create their own books for assessments and demonstration of learning. The platform offers a plethora of templates ranging in comic book style to a more sophisticated magazine aesthetic for developing young writers looking to add something dynamic to their portfolio.
While there are downloading and printing capabilities to create permanent artifacts for teachers and students, most Book Creator users take advantage of the audio, visual, and hyperlink opportunities for interactive digital products. The site and app’s bank of shapes, graphics, and fonts takes off some of the design pressure, but users can also enjoy importing their own photographs, audio, and video to customize their projects.
Elementary Benefits
Improve Literacy
K-5 teachers love Book Creator for improving their students’ foundational literacy with the digital edge. Book Creator works seamlessly with iPads for those elementary classrooms equipped with iPads or tablets. Young readers will appreciate the new Read-to-me feature on Chrome which allows students to click on the word or phrase and have that unfamiliar word read aloud. Teachers can also read and record their own books that they have created, which can be especially advantageous while students are working through stations. Being able to hear their teacher read stories to them at their own pace will build their autonomy, with natural differentiation.
Reuse and Adapt Resources
Book Creator allows teachers to create books and resources that will serve them across curriculum and time. For instance, teachers could create a book to reinforce concepts of phonics, like this example here, while also serving as a frontloading and preview activity for a science lesson. Teachers can use these books from year to year with ease, as the platform allows you to edit content, updating with new videos or other fresh, relevant content.
eBooks Elevate Engagement
Elementary teachers may also find that the eBook format simply engages students at a higher level than traditional books. Because students can intermittently watch the embedded videos or hear occasional supplemental sound effects, they’ll be more likely to sustain longer reading intervals. While there is a time and place for physical books, there is no doubt that eBooks have the interactivity element that so many digital native learners crave.
Secondary Benefits
Learning through the eBook Production Process
At the secondary level, students can benefit from the creation features of Book Creator. By creating an eBook, students are engaging in a multi-step, complex writing and design process that is sure to improve their stamina and patience. They’ll inherently have to make many written and visual rhetorical decisions to properly engage their reader, either informing or entertaining them. Many secondary teachers today find that they get stumped in determining what product students will create, with some products feeling contrived or dated. An eBook on Book Creator serves as an outlet for authentic publishing on a prolific educational publishing site. When students see examples on Book Creator’s site from other middle and high school level students, they’re bound to be inspired.
Embedding Creativity
Fostering creativity at the secondary level has never been more important. Teachers around the world are considering how to infuse opportunities to allow their students to show their understandings in more creative and dynamic methods. In his blog, Sam Kary provides some great examples of assessments that could seamlessly translate to using Book Creator. For instance, students in a social studies or ELA class could write a biography of a historical figure and publish an eBook to share with their classmates in a virtual gallery walk. Through the writing and design process, students will practice informative writing skills, integrating, linking and properly citing sources, and considering audience engagement as they design the sequence of the book.
A Sense of Community
Book Creator also provides endless opportunities for collaborative writing for students. Teachers, too, have access to student projects so they can offer valuable feedback in real time. Middle or high school teachers may consider units where the class could curate a collection of their writing. For instance, Book Creator houses lots of examples of poetry collections. Students across a class, building, district, or even cross-school could produce collections of poetry organized by theme, style, or any other focus based on the curricular focus. When students see that their contribution makes up a bigger whole, they are more likely to go the extra mile.
Digital Portfolios
Increasingly, colleges and post-secondary institutions are seeking robust student portfolios that showcase the students’ digital content creation ability. Students can certainly embed their Book Creator eBook’s within a digital portfolio (like a Google Site) or they can use Book Creator to create the actual portfolio. Each page, then, becomes the space for students to link the work, write up a reflection, or explain the creation process behind the piece. By compiling a sophisticated and organized collection of their own work, they’ll be sure to stand out to wherever they are applying.
Sharing with Ease and Pride
Whether it’s a teacher publishing an eBook for a one-day lesson or a student creating an eBook that captures their work from an entire school year, Book Creator is allowing educators and young people to produce stand-out work. With an intuitive and user-friendly interface and a continually evolution to be on-trend with updated aesthetics, apps, and extensions, Book Creator is clearly in tune with what contemporary classrooms need today. It provides a fun space to produce eBooks that can be shared with pride.

Social-Emotional Learning is gaining momentum in schools worldwide. This educational method is meant to be integrated into the curricula to provide teachers and parents with tools to support the mental health and well-being of students. Research on SEL shows telling evidence of improved academic performance and behaviors among students.
The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL), a leading organization dedicated to making Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) part of education, defines SEL as “the process through which all young people and adults acquire and apply the knowledge, skills, and attitudes to develop healthy identities, manage emotions and achieve personal and collective goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain supportive relationships, and make responsible and caring decisions.”
The organization identifies five core competencies that comprise SEL, which are self-awareness, self-management, social awareness relationship skills, and responsible decision-making. All five are critical for the success of students in and outside the classroom. While there are multiple ways to integrate SEL into the curricula in traditional ways, many apps, games, and web resources can make SEL more engaging and effective for students.
Here is a list of excellent tools and resources that will help you address the five core competencies of SEL.
Self-Awareness is one of the key components of SEL and is the ability to be aware of our emotions, needs, values, preferences, thoughts, attitudes, strengths, etc., and how these may impact our lives from small day-to-day activities to bigger life decisions.
An excellent way of cultivating self-awareness in the classroom is to start each day with an emotional check-in. This can be as simple as a journaling activity asking students questions such as “What are some of your feelings right now?” and “Where are they coming from?” or having them share their emotions through emojis on Google Jamboard.
Alternatively, you can introduce short meditations to your classes. There are lots of meditation tools such as Calm and Headspace. A full body scan meditation on Headspace can be a great warm-up for teaching students to pay attention to how their bodies store emotions. If you are looking for something designed specifically for children, check out DreamyKid. It is a meditation app designed for kids ages 3-17 and is used by hundreds of schools worldwide. The app aims to bring mindfulness to schools through meditations, affirmations, guided journeys, healing activities, and other tools. DreamyKid recently introduced a school program that costs $32-$47/month with a 10-month commitment and provides flexible pricing options depending on the number of teachers who integrate it into the classroom.
Self-Management
Self-regulation and management of our emotions are essential for our mental and emotional well-being. This component of SEL implies learning to manage and regulate emotions, actions, and choices, manage stress, and set goals.
In teaching our students and kids to identify and process their feelings, we set them up for success in an increasingly stressful world. You can teach students to identify their emotions and those of others through games and interactive activities. Nearpod, a platform offering thousands of educational videos, ready-made lesson plans, and interactive material has excellent CASEL-aligned teaching resources that can assist you in bringing SEL to your classroom daily. Use this Nearpod video that explains how to identify anger and have students take the quiz afterward.
Social Awareness
Social Awareness is a competence rooted in empathy and concern for others. It is the ability to put ourselves in other people’s shoes and see things from another perspective. This can be easily modeled and practiced through games focusing on conflict resolution.
Cool School: Where Peace Rules may be the ultimate tool for this. The game helps cultivate empathy by engaging kids in various scenarios that ask them to put themselves in another person's shoes. Play this game to give students the opportunity to resolve conflicts in an empathetic way and in a safe environment.
Relationship Skills
SEL develops students’ relationship skills helping them to effectively manage their interactions in and outside school. To develop interpersonal skills, respect, and empathy for others.
If you are teaching middle school, consider incorporating Middle School Confidential, an award-winning graphic novel series by anti-bullying activist Annie Fox. This tool will engage students in interactive reading activities while helping them navigate middle school with increased emotional preparedness and empathy. For instance, by choosing the Middle School
Confidential 2: Real Friends vs. the Other Kind, you can teach students how to make friends and manage tough social interactions, resolve conflicts, and deal with gossip, bullying, and other issues.
Middle School Confidential 1: Be Confident in Who You Are will help strengthen students’ self-esteem and teach them empathy and other tools to manage situations involving teasing, bullying, or self-doubt.
Responsible Decision-Making
Responsible decision-making is SEL’s fifth competence. To address this aspect of SEL, introduce story ethical decision-making through games such as Quandry. Quandary, a free non-profit educational tool designed for students 8+ can help “develop critical thinking and perspective-taking, practice empathy, and learn to make ethical decisions through fun and engaging gameplay.” Quandary helps develop critical thinking and responsible decision-making skills by asking students to identify and resolve real-life issues. The game claims research-based evidence for an increase in fact vs. opinion comprehension, self-reported perspective-taking, concern for others, and overall high student engagement.
A similar decision-making game that can be integrated into your classes is Life Choices, a life simulation game that requires students to make choices to help a fictional town with repairs and restoration. Rather than focus on right or wrong decisions, the game creates an opportunity for students to make ethical decisions through real-life situations.
Conclusion
Social-Emotional Learning becomes more and more necessary as we face constantly changing educational environments. Rather than allow digital tools and devices to consume our student’s attention and affect their mental and emotional health, we can instead use them to bring gamification and storytelling into the classroom to foster their social and emotional development. With so many helpful SEL resources available in our toolkits, we can prepare future generations that are well-equipped to tackle any challenge that shows up on their life path.

Introduction
Many students that require additional education support are familiar with the services of tutors; however, just as technology has evolved over the years, so has access to educational support systems. While traditional tutors offer in-person or virtual sessions and use their area of expertise to support students, technological advances have supported a rise in options for students seeking advice and assistance. The problem is that many students needing educational support may receive appropriate support through the services of an educational coach. However, more awareness is needed in higher education to connect students to the resources and support systems that fit their academic needs. This article presents the benefits of expert coaches as an alternative to traditional tutoring. Just as education has evolved with technology, new advances in educational support systems have evolved to support the various learning needs of students.
Background
Over the years, students in higher education have had access to tutoring services. At some institutions, tutoring services are included in the tuition and are freely available to all students. However, many universities only offer a writing lab as a free option, leaving many students to pay for tutoring services. Despite having access to educational support, many universities have noted barriers to accessing tutoring. For example, researchers Ciscell et al. (2016) shared that there is a stigma of poor intelligence associated with using a tutor, which has prevented many students from seeking help, even when the students would benefit from the services. These researchers also noted that student self-perception also heavily influences how students may or may not seek help. For example, if students believe that they cannot change their habits or style, they may be less inclined to seek assistance.
While in-person tutoring has many benefits, how do administrators and faculty support the students that need an alternative to traditional tutoring? The pandemic has helped advance educational technology and support, presenting traditional and non-traditional students with various support resources. For example, using a quantified learning approach via expert learning coaches may be the solution that many of today’s students need.
Current Best Practices
The idea of quantified learning is not a new concept; rather, it is a term that has progressed with the needs of students over the years. Zubair Talib (2020) defined quantified learning as “the use of technology to help provide more granular and predictable education and education outcomes.” Personalized learning and personal development can be achieved through quantified learning. Considering the needs of consumers (students), learning engineering, learning analytics, and adaptive learning are the main components that support quantified learning services.
In an article by Baker et al. (2018), researchers explained how engineered learning “applies a rigorous combination of theory, data, and analysis to develop and improve educational systems and methodologies to produce enduring and high‐quality learning” (p. 3). Learning engineering is being used by researchers and developers to create next-generation learning tools. One example is supporting human processes through the development of integrating computer-based tutoring with human tutoring.
Another component of quantified learning is learning analytics. Tsai (2022) explained how learning analytics is “the measurement, collection, analysis, and reporting of data about learners and their contexts, for purposes of understanding and optimizing learning and the environments in which it occurs.” In other words, data is collected on learners to understand how and why they learn in certain ways. This data is then used to develop new resources to support the learner’s needs.
The final component of quantified learning is adaptive learning. According to Radboud University (2022), adaptive learning is the use of technology using a form of artificial intelligence to identify, diagnose, and provide feedback based on student knowledge and performance. For example, an online language learning program may be able to assess a student’s current knowledge and mastery of a language and recommend a specific path of learning using the pre-determined factors. Another example is how many K-12 schools are testing and implementing assessments that use adaptive learning technology. As a student progresses through an assessment, the AI determines the level of understanding and provides easier or harder questions based on student responses.
Some of the most prominent educational companies that use quantified learning include Khan Academy, Duolingo, and Udacity. Khan Academy offers students various lessons and interactive activities to support learning needs and specific concepts. Duolingo is a language learning platform that supports learning a language through activities and games. Finally, Udacity is a platform that offers a variety of massive online open courses (MOOCs) to support mastery of several topics without the commitment level of a university course.
For companies that support education, there are several factors to consider when developing quantified learning. Collings and McMakin (2021) explained that companies need to plan their learning and development to reflect predicted skills students will need in the future.
Expert Coaches and Quantified Learning
Universities are also investing in adaptive learning technologies that support personalized student support. For example, the University of Texas developed the UT Total Educational Experience or TEx. The TEx is an adaptive learning system that uses student performance to personalize student support. For example, the TEx program can provide suggestions for advising, coaching, and mentoring with each program a student is taking.
Adaptive learning technology is already in use and supports the learning needs of students in various settings and at various levels of education. However, how can students access a combination of customer service with curricular content tutoring? Expert coaching is one way to address the needs of students that need support in their academic studies but may not need the level of personalization that a tutor provides. For example, an academic expert coach could use student input from an educational AI-based program to gather information on an assigned report, resources needed, and guidance required by the student. Coaches would use the information supplied to guide the student to the needed resources (books, journal articles, professional organizations) and provide a guide on how to complete the assignment using the course requirements. Some examples of programs that match students to expert coaches or tutors include Brainly and MyTutor. Through adaptive learning programs, expert coaches do not need to be experts in one specialty. Instead, they can use a combination of computer-based support recommendations with basic academic knowledge and understanding to guide students seeking curricular support.
Conclusion
Advances in technology have evolved to provide students with personalized instruction and support. Quantified learning has also transformed the possibilities of educational support services. Through research and development, many educational companies have developed AI products and adaptive learning technologies that offer students personalized support. While traditional tutoring is still effective for traditional students, other options are necessary to support the learning needs of non-traditional students. Expert coaches are an appropriate alternative to traditional tutoring. Expert coaches use AI-supported software to collect student data and create personalized academic support, providing a new means to learning success.
Sources
Baker, R. S., Boser, U., & Snow, E. L. (2022). Learning engineering: A view on where the field is at, where it’s going, and the research needed. Technology, Mind, and Behavior. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/tmb0000058
Ciscell, G., Foley, L., Luther, K., Howe, R., & Gjsedal, T. (2016). Barriers to Accessing Tutoring Services among Students Who Received a Mid-Semester Warning. Learning Assistance Review, 21(2), 39-54. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1114513.pdf
Collings, D., & McMakin, J. (2021). The practices that set learning organizations apart. MIT Sloa Management Review. https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/the-practices-that-set-learning-organizations-apart/
Online Education. (2022). Adaptive Learning: How Online Colleges Tailor Programs to Student Needs. Online Education. https://www.onlineeducation.com/features/adaptive-learning-online

Blogging has been a part of the internet since the beginning. It has so much potential that has never been fully utilized in the classroom. This post will give you ideas on how to use blogs effectively in the classroom, and it will also give you practical tips on how to set it all up on the technical side.
"Blog" is short for weblog. It is seen by most as a social media of some sort and ultimately, non-academic. But blogs can ultimately be a force for good in the educational space with the correct approach.
Why would I want my Students Posting or Reading Blogs?
Blogs can be used in many ways. In the classroom, a blog can be written by teachers, or by individual students. We definitely recommend you let your students maintain their own blogs.
When students start writing blogs, they begin putting their writing skills, and creative thinking to the test. It is easy to read posts but writing completely new posts is a different beast to tame. This will help your students recognize good writing online, and they will be made aware of constructive interactions online. A blog will also serve as a creative outlet for many students who are otherwise frustrated without an outlet in their class.
You as a teacher can also maintain a blog of yourself. A teacher’s blog can be used to publish assignments, and resources required in the classroom. It can also be used as a place to keep all the parents up to date on what is happening in the classroom.
What would my Students Blog About?
There are many different genres of blogs on the internet. You could also argue that there is an infinite genre of blogs limited only by the imagination. In this section, let us go through some good blog ideas.
The first type of blog is a single project blog. In this type of blog, a student can maintain a single blog for the duration of a project. The blog would start with the inception of an idea. It would contain all the research conducted on the topic. Then it can document the process of getting the project done. Then it would end with the outcome of the project and the advantages and disadvantages of doing it. This type of blog would be perfect for a long-term assignment.
The second type of blog is a blog for special interests. This blog would only feature a certain interest of the student that authors it. It can be anything that interests the student, from Legos to fighter jets. It would help the student improve their research skills, and also improve their ability to condense their love for something into words. Students love to work on something they have an interest in, so this has the potential to be an automatic favorite with the kids (unless they hate writing).
Another type of blog is termed the portfolio blog. This blog serves as a portfolio of all the work a student works on. It can have all the stories, essays, and poetry authored by the students. You can create a single blog to showcase all the students' work online for parents and the general public to read, or you can ask every student to create their own portfolio blog.
A journalistic blog is a type of blog that is more of a news source than anything else. This blog can include news from the school, classes, teachers, or anything of interest happening. This type of blog will serve as an excellent way to inform parents about the current situations in the school.
A blog can also be a place to review things. Students can use the blog platform to review movies, games, or food. If a student wants to talk about their favorite game at length or talk about the vacation they took to a distant place, this blog can provide that creative outlet.
A how-to blog can allow students to help each other online. A student that is good at math can make posts on how to solve certain problems, another student might write a post on how to understand a certain concept taught in the class. There are unlimited ways in which how-to blogs can prove helpful.
How do I Get Started?
Blogging can seem daunting, but it is not that difficult with the abundance of blogging sites on the internet nowadays. If you want to help every student sign up for a blog, you might need to ask for the help of the IT department. The following sites are some good choices to create blogs.
WordPress is the most widely used blogging site in the world. Anyone can simply sign-up and use their templates to create blogs. There is no technical hassle, or anything complicated with this website. It is highly recommended.
Edublogs is a website that allows teachers to create their own blogs to manage their classes. They boast that they have “a ton” of features, themes, and plugins that are geared toward education. If you are a teacher looking to create a blog for yourself, then this website is highly recommended.
Fanschool is a website that allows students can publish in a safe environment moderated by teachers. If you want a space that keeps students safe from the harms publishing works to the public can provide. If your educational institution has decided to make blog posts of students private, then this is definitely recommended.
Conclusion
Blogs fall under the category of social media, but they can prove to be a force for good in the classroom. It can be a source of creative outlet for students that need it, and it can be something fun that students will love to do. Teachers can maintain blogs themselves, or make their students maintain their own blogs. A blog can be for a single project, special interests, portfolios, journalistic in nature, reviews of things, or a how-to blog. Setting up a blog is very simple with the abundance of websites like WordPress, Edublogs, and Fanschool.
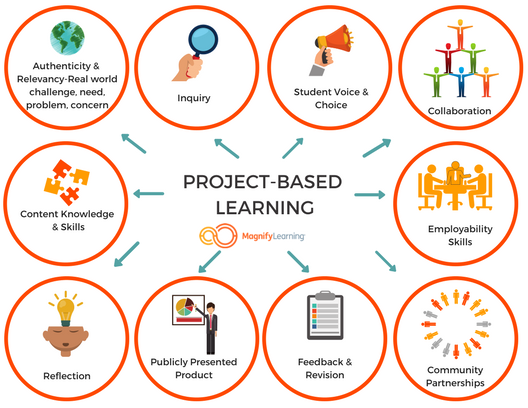
Introduction
Project-based learning is one of the hottest trends in education today. This style of teaching has been used for decades but has gained popularity in recent years as educators have begun to realize its benefits. The potential of project-based learning to improve academic performance, career prospects, and life opportunities is leading many schools to switch over to it.
The purpose of this article is to examine the benefits of project-based learning and how it can be incorporated into classroom settings. Let's begin!
What Is Project-Based Learning?
John Dewey, an American philosopher and educator, is credited with developing PBL. PBL (project-based learning) is an instructional approach that offers students an opportunity to develop knowledge and skills through engaging projects that are based on real-world challenges and problems. For an alternative definition check out this article from PBLWorks.
PBL Is More Student-Centric Than Traditional Learning
In PBL, the students are more engaged, motivated and involved in their own learning. The teacher acts like a facilitator who helps them along the way. This can also be referred to as personalized learning. PBL involves students as leaders and decision-makers in the learning process as opposed to teacher-centered approaches. For more details on student centered learning check out this article.
PBL Can Improve Students Retain Information Better
PBL helps students retain information and skills longer. Instead of learning facts and procedures in isolation, PBL teaches students how to apply their knowledge in new situations. Rather than simply memorizing the steps for solving a math problem or constructing a paragraph, they learn how to use their knowledge of basic concepts like fractions or parallel prose sentences to solve real-world problems.
For example: How many volunteers does it take to keep track of all the ingredients at an event? How many slices can we make from this loaf?). Once they’ve developed these transferable skills, they can apply them again when faced with future challenges—and thus continue building on them throughout their academic career.
PBL Can Help Improve Students’ Essential 21st-Century Skills
PBL is a great way to help students develop their essential 21st-century skills. These skills are not only important for college and career readiness, but also for life in the digital age.
These essential skills include:
Problem-Solving: PBL requires students to identify an issue or dilemma, then gather information and form solutions. This is exactly what they will be asked to do when they enter the workforce or pursue higher education.
Cognitive Flexibility: In addition to being able to solve problems using logic, it's equally important that students be able to think outside of the box if they want to succeed in today's constantly changing world. PBL gives them this opportunity, as well as time away from technology so they can focus on human interaction and creativity without constant distraction by social media sites like Facebook or Instagram (or video games).
Critical Thinking: Asking questions is an essential part of any problem-solving process—and critical thinking involves questioning everything! Ask kids why something works a certain way instead of just accepting it; encourage them not just ask "why" but also "how" as well (i.e., "Why does this happen?" vs "How does this happen?"). This will help them better understand how things work—and might even lead them toward future careers where these skills come into play most often such as healthcare (doctors), engineering/science (engineers), business management(managers).
PBL Can Help Students Learn To Manage Their Time Effectively
PBL requires students to manage their own time, which means that they will learn how to plan their days and weeks, as well as how to prioritize when things come up. This is a skill that we hope our students will take with them into adulthood, because it's important for them to be able to manage their own learning.
PBL Can Help Students Maximize on Available Resources
PBL aims to help students understand how to use resources available to them. In a classroom where PBL is used, students will be encouraged to use multiple sources of information when they complete projects. They'll also be required to find and use their own resources as well as those provided by the teacher.
The following are examples of types of materials that could be helpful in completing a project:
- Books;
- Websites and databases (such as encyclopedias);
- Other people (for interviews or information).
Project-based learning lets students make real-world applications of knowledge, which might improve their career prospects later on. If you’re looking for great tips on how to successfully integrate PBL then check out this article.
Project-based learning is a unique approach that has been gaining popularity in recent years. It involves students creating their own projects, which they can apply to real-world situations and may even improve their career prospects later on. How does PBL help students make real-world applications of knowledge? And what are some examples of real-world applications of knowledge?
Planning
There is a lot of planning involved in implementing project-based learning in a classroom setting. You will need to plan the lesson, plan how the students will complete their projects and then follow up with them after they are finished. This can be done through grading or giving comments on their work, asking questions about their process or research methods.
Assessment
To assess a student's progress, it is important to have assessments that are relevant to the project. If students are working on a fictional story, then an assessment should be written in the same format as their story. The teacher may also want to ask students questions based on their storyline or ask them about specific details within their writing. The teacher can create problems that require math skills or history knowledge if these topics are relevant to the project as well.
It is also important for teachers who teach through project-based learning tactics, such as Project Based Learning Online (PBLO), to give frequent assessments so they can gauge how well each student understands what they have learned and what they still need help with. This will allow instructors at all levels of education from preschool through high school classrooms as well as colleges and universities across North America find out which concepts are difficult for them yet easy enough for everyone else in class without wasting too much time teaching something else.
The benefits of project-based learning are worth overcoming the challenges it presents.
Sometimes, there are just too many things that can go wrong when implementing project-based learning in a classroom. You need to have a good teacher and a student population with the ability to work independently. The curriculum has to be appropriate for your grade level, and you need support from the administration of your school. But even with all of these things in place, some students might not be able to manage their workload or keep up with their peers.
If you're considering implementing project-based learning at your school but aren't sure how it will work out for you, take some time before beginning the process by thinking about what needs to be done differently compared to traditional classrooms. This way, when challenges arise during implementation (and they will), you'll know how best to move forward as quickly as possible without sacrificing quality education for all students involved!
For some great tips on how to design your own PBL curriculum feel free to check out this great article on the TechnoKids website.
PBL Helps Students Develop Various Skills
PBL develops academic, social, and ethical skills. According to the Association for Project-based Learning (APBL), “PBL encourages higher order thinking through problem solving and collaborative learning, which are essential 21st century skills.” Students learn how to take responsibility for their own learning and how to communicate effectively with others in a group setting. They also develop a sense of accountability for themselves and their work by seeing that it has an impact on their community or society at large (and isn't just about pleasing teachers).
PBL Improves Test Scores and Student Results on Other Assessments
What do you think? Does PBL help students learn better, even if it's not measured by standardized tests? The jury is still out on this question. It's possible that the skills and knowledge learned through PBL may not be directly transferable to other types of assessments. There are a few excellent reasons why we should continue to encourage project-based learning in our schools.
First and foremost: PBL can help students develop their critical thinking skills. This skill is invaluable when students need to think critically about complex situations outside of school as well as inside of school (for example, in debates).
Second, participation in PBL allows students and teachers alike to engage with real-world problems and challenges through authentic experiences and challenges—instead of being limited by standardized tests that only test one kind of knowledge against another kind.
Third, when students have more agency over what they're learning (rather than simply being presented with facts), they tend to retain more information long-term because they actually care about what they're learning! If you’re curious about which tools are essential for PBL then look through this informative post.
Student Motivation and Attitudes Towards Learning
Students who engage in PBL are more motivated, engaged and engaged with their school work than students who do not. Students who engage in PBL are also more likely to want to learn, and to want to continue learning; they are more likely to be self-directed and self-motivated as well as having a positive attitude towards learning.
Conclusion
We hope that this post has inspired you to try project-based learning in your classroom. For teachers, PBL can be a great way to engage students and give them the chance to apply new knowledge. It's also a useful strategy for preparing students for the real world—and it might even help improve their career prospects later on! We think the benefits of PBL are worth overcoming the challenges it presents. Assessing student progress with project-based learning can prove to be difficult, but with careful planning and continued collaboration between teachers and students, PBL can have positive effects on student motivation and attitudes towards learning.

There are many ways to make learning fun and interactive for teachers, students, and even parents. That’s why apps like Remind have been made specifically to ensure seamless and secure interaction between teachers, students, and parents. As many learning institutions embrace the hybrid mode of learning, it is imperative that teachers choose the best apps to complement their teaching and improve their interaction with students and parents.
Let’s look at why Remind should be on top of your education apps if you are a teacher and how you can use it to foster collaboration and interaction in the classroom.
What is Remind?
Remind is an app and website platform where teachers can share resources and communicate by sending secure messages to different recipients. These could be students, parents, or other teachers.
It makes collaboration among teachers and students easy as this can be done directly to an entire class or different sub-groups. The different classes or sub-groups are differentiated by unique codes sent via text or a link to the target members to sign up. For example, you could invite students to join your foreign languages class or parents to join the monthly class meeting group.
As a teacher, you can manage up to 10 classes and have as many students and parents added to your group. You could also add other teachers to the group. For younger students, their parents could use their email for joining hence being part of the conversation and also monitoring conversations.
Ways Remind is revolutionizing Interaction in the Classroom
Scheduling Reminders
Reminders are great for managing deadlines. Whether for assignments, school activities, teachers’ or a parents’ meeting, sending out reminders is a great way to keep everyone engaged and getting things done at the right time. For example, this fantastic Remind feature could be used for organizing a school trip, reminding students about a quiz or test, reminding parents about a class meeting, or communicating scheduling changes for events and other activities.
Sharing Classroom and Professional Development Resources
Interactive learning is gaining prominence with the advancement in technology. With Remind’s stamps feature, teachers are now able to share classroom and further learning resources in the form of text, pictures, links, videos, and other files on the platform for students to access.
Stamps could also be used to share quizzes and ask students about their opinion on different learning topics. You could make it interesting by sending students some warm-up questions or trivia before class. Better yet, you could share links with other teachers to different professional development resources.
Engaging with Parents
Well, wouldn’t it be nice if parents are made part of their children’s learning journey? That’s how Remind bridges this gap by allowing teachers to share important resources or information directly with parents. For example, parents could be added on the classroom Remind platform to view projects done by the students, or access further resources to help them understand their children’s learning journey.
A teacher could also send messages directly to parents regarding their child’s behaviour and learning progress. Through the stamps feature, parents could also share feedback or recommendations on what they feel could improve the learning outcomes of their students.
Fostering Collaboration Among Students
Apart from using Remind in the classroom for communication between teachers and students, a teacher could create a more collaborative environment by allowing students to message each other on the platform.
To make it interesting, you could divide the students into different sub-groups and let them choose a team leader to spearhead the discussions. This is a special feature that would enable students to hold discussions on different topics or assignments. It also gives them time to research further outside the strict classroom hours, gaining a better understanding of the topic under discussion.
One great feature about Remind is the ability to pause a conversation. If you feel that students are taking too much time on the platform outside classroom hours, you could pause the discussion. This means that no one will be able to reply or add comments, until a time when you as the teacher deems necessary to continue the discussion.
Enhancing Secure Communication
In this era of cyber-attacks and the push for data privacy, Remind, unlike other communication platforms, offers a more secure way of interacting with your students or parents. How is this possible?
When parents or students sign up for your course or join your group, they will appear on your list, however, none of the participants will view each other’s contact information. This prevents incidences where group members take someone’s details without their consent and minimizes the risk of receiving unsolicited messages.
Making Learning Visual and Interesting
The stamps feature is so powerful that it brings a whole vibe into the classroom setting, doing away with the monotonous slides and dictation as is usually the norm. When a teacher shares a question or quiz, students can reply with stickers and other fancy icons and symbols like stars that add functionality to the content and make it more visually appealing.
This would be very ideal especially if running a poll on what topics your students would want more emphasis on or short quizzes that don’t require lengthy responses. Another feature that makes it interesting is the ability to get transcripts of the conversations or activities carried out on the platform. So, if you were running a poll, you can share the results directly with your students.
Also, the fact that you can link the platform to other third-party platforms like zoom or google meet makes it more interesting as students, teachers, and parents can hold live virtual events right through the Remind platform.
Conclusion
Interactive classrooms or learning environments are always every teacher’s dream. Thanks to platforms like Remind, this is now a reality.
From sending reminders, sharing learning resources, to communicating with parents, the options are limitless with Remind. Remind should be a priority app on any teacher’s list because of its simplicity, effectiveness and it’s free. Of course, there are other optional premium features that would enhance the platform experience but you can start with the free version.
If you are ready to start using the platform, check out these steps and follow the onboarding guide to help you get started and hopefully achieve the classroom of your dreams.
Introduction
Each day, cutting-edge information technologies provide us with new ways of tackling challenges in and outside our classrooms. Along with these rapid enhancements and solutions comes the challenge of staying up to date with current developments.
In a digitally enriched world where messaging apps and social networks have replaced face-to-face communication, where collaboration happens in real-time and online, and information is obtained via digital libraries, vlogs, and video content, digital literacy is becoming a fundamental skill to promote through our courses.
What is digital literacy?
While there is a plethora of definitions for digital literacy, it can be defined as “the ability to use information and communication technologies to find, evaluate, create, and communicate information, requiring both cognitive and technical skills” (National Digital Inclusion Alliance). Digital literacy in the classroom comprises a set of skills that allow students to use digital technologies to obtain and evaluate information, solve problems, complete assignments, and create content.
How can teachers in humanities promote digital literacy and digital citizenship as they assist students in developing essential skills such as communicative and collaborative abilities, critical and analytic thinking, creativity, and social responsibility?
Here are five ways to foster these skills while incorporating digital literacy into your classes.
- Enhance media literacy
One of the vital skills in digital literacy is the ability to tell fact from fiction and become conscientious and critical users of information resources. To encourage this, you can have students analyze different pieces of information, provide a critical reading of an op-ed article on history, analyze a blog post on ethics or complete a fact-checking assignment for a news piece. To further aid students, you can provide them with media literacy toolkits or organize workshops on detecting misinformation, decoding media messages, fact-checking, or the ethical use of online resources. Additionally, class discussions on digital literacy can revolve around how certain media outlets can empower different groups of people or vice versa. And this takes us to our next point: digital equity.
- Advocate for digital equity
Apart from the skillful use of digital resources, digital literacy also implies students’ awareness of the digital divide and how each of us can contribute to digital equity. The National Digital Inclusion Alliance defines digital literacy as “a condition in which all individuals and communities have the information technology capacity needed for full participation in our society, democracy, and economy. Digital equity is necessary for civic and cultural participation, employment, lifelong learning, and access to essential service.” For your classes, you can create opportunities for students to research digital equity in their community, complete research assignments on how digital inequity affects certain groups, find ways to advocate for digital equity and amplify stories by and about underrepresented groups. Whether teaching history, literature, or cultural studies, have students consider how histories and stories of underrepresented people are being told and disseminated in today’s digital landscapes.
- Encourage digital storytelling
Another way to develop digital literacy in students is to encourage and empower them to become creators. Digital storytelling can be an excellent tool for this. It will not only support students in putting their creativity to work but will foster 21st-century skills. This way, students will become more aware of the intricacies of creating a digital piece of information and ask important questions: What responsibilities do creators have? How do our stories and voice influence and empower people?
Students can hone their digital storytelling skills by creating video essays or presentations through digital tools such as Sutori. You can incorporate digital storytelling into a wide range of humanities classes from Creative Writing to Arabic and Classics. Here’s an excellent list of digital storytelling resources put together by the University of Wollongong in Australia.
- Assign multimedia research projects
Switch the traditional final research paper assignment with a multimedia research project where students can critically examine and analyze multimedia pieces related to the topic they want to explore in their final paper. This assignment will not only engage students more creatively but will allow them to share their work with classmates or the entire school via a class blog, for instance. A digital research project will also encourage students to think broadly, interact with a variety of digital tools, and foster interdisciplinary connections. For instance, a final project for a history or literature class could focus on the baroque art movement in music, literature, and painting and have embedded links to podcast episodes, music videos, online galleries, photographs, and other resources exploring this topic.
- Foster online communication and collaboration
Good communication and online collaboration play a vital role in an increasingly digital world. Yet, the online space can be an intimidating and unsafe environment for many, so it is important to educate future citizens who are equipped with the skills and awareness to contribute to the creation of safer online spaces. Whether you are teaching online or face-to-face, consider creating online debates or discussions using your LMS to allow students to practice safe and respectful interactions with diverse opinions and ways of thinking in an online environment. After the assignment, guide students to reflect on the challenges of communicating and collaborating in online space and the tools they used to communicate respectfully and effectively. Make sure you share and discuss netiquette rules with your students before assigning the activity.
Conclusion
Digital technologies will continue evolving and intersecting with every area of our life and work. To set up our students for success in this digitally driven world, we need to aid them in becoming digitally literate and active contributors to a more democratic, ethical, and safe digital environment.


